You’ve probably heard about L-arginine’s potential benefits for heart health, athletic performance, and circulation—but knowing how to take arginine supplement correctly is crucial for experiencing those benefits safely. Many people make simple mistakes with timing, dosage, or form selection that significantly reduce effectiveness or create unnecessary risks. This guide cuts through the confusion with precise, actionable instructions based on medical evidence. Whether you’re considering arginine for blood pressure support, workout enhancement, or general wellness, understanding the proper administration method makes all the difference in your results.
Learning how to take arginine supplement properly begins with recognizing that this semi-essential amino acid works differently than many supplements. Your body naturally produces L-arginine but often requires additional intake through diet or supplementation—especially when pursuing specific health goals. The “L” designation indicates its free-form structure, allowing for efficient absorption when taken correctly. Before adding this supplement to your regimen, you need clear guidance on form selection, dosage calculation, timing strategies, and safety considerations that most generic articles overlook.
Selecting the Right Arginine Supplement Form for Your Needs
Choosing between oral capsules and intravenous administration determines your entire supplementation approach. For 99% of users, oral L-arginine supplements in capsule or tablet form represent the practical choice—available over-the-counter and suitable for home use. These provide precise dosing in standardized amounts, eliminating guesswork with clear label instructions. When learning how to take arginine supplement orally, note that capsules typically contain pure L-arginine powder while tablets may include binding agents that slightly affect absorption rates.
Intravenous L-arginine (marketed as R-Gene 10®) delivers the amino acid directly into your bloodstream under medical supervision. This method ensures complete bioavailability and rapid effects but requires professional administration in clinical settings. Unless your doctor has specifically prescribed IV treatment for a diagnosed medical condition, oral supplementation will be your appropriate route. Never attempt IV administration at home—this requires trained medical personnel to monitor for potential reactions.
Calculate Your Exact Arginine Dosage Based on Health Goals

The most common mistake people make when learning how to take arginine supplement involves improper dosing. Therapeutic doses range from 6 grams to 30 grams daily, but your specific needs depend on your health objectives. Start with 3-5 grams daily for general wellness, gradually increasing to 6-9 grams if pursuing cardiovascular benefits. Athletes seeking performance enhancement often use 6-12 grams daily, split into multiple doses.
Never consume your entire daily dose at once—divide it into three equal administrations spaced throughout the day. For example, if targeting 9 grams daily, take 3 grams with each meal. This strategy maintains stable blood levels while minimizing digestive discomfort. Crucially, never exceed 30 grams daily without direct medical supervision, as higher doses significantly increase side effect risks. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting to determine your personalized dosage based on health status and goals.
How to Adjust Dosage for Maximum Effectiveness
Begin with a conservative 3-gram dose for the first week to assess tolerance. If no digestive issues occur, increase to 6 grams daily (2 grams three times daily). Monitor your body’s response for two weeks before considering further increases. Those using arginine for specific therapeutic purposes may require 9-12 grams daily under medical guidance. Remember that more isn’t always better—your body can only utilize a certain amount of L-arginine at one time, making divided dosing far more effective than single large doses.
Optimal Timing Strategies for Different Health Objectives
When to take L-arginine dramatically impacts its effectiveness for your specific goals. For general cardiovascular support, take your divided doses with meals—breakfast, lunch, and dinner—to minimize stomach upset while ensuring steady absorption. The food helps buffer the supplement, reducing common digestive side effects while maintaining consistent blood levels throughout the day.
Athletes seeking performance benefits should time one dose 30-60 minutes before workouts to enhance blood flow and nutrient delivery to working muscles. Many experienced users split their pre-workout dose—taking half 60 minutes before and half 30 minutes before exercise for sustained effects. Post-workout administration (within 30 minutes after exercise) may also support recovery by improving circulation to fatigued muscles. Consistency matters more than perfect timing—establish a routine you can maintain daily for cumulative benefits.
Combine Food Sources with Supplements for Best Results
Understanding how to take arginine supplement effectively means recognizing that dietary sources should complement, not replace, strategic supplementation. Beef, poultry, pork, and seafood provide excellent natural arginine sources—just 3 ounces of turkey contains about 1.6 grams. Plant-based options include almonds (1.5 grams per ounce), walnuts, peanuts, and legumes like chickpeas.
While food sources help maintain baseline levels, they rarely provide therapeutic doses for specific health goals. A balanced approach works best: maintain a protein-rich diet while using supplements to reach your target dosage. For example, if your goal is 9 grams daily, dietary sources might contribute 3-4 grams, requiring 5-6 grams from supplementation. This combination approach ensures you benefit from the additional nutrients and fiber in whole foods while achieving precise dosing through supplements.
Recognize Realistic Timeframes for Seeing Results
Patience proves essential when learning how to take arginine supplement properly—effects don’t happen overnight. At minimum, L-arginine requires 24 hours to absorb and begin exerting measurable effects. However, most users won’t notice significant benefits until after 2-4 weeks of consistent use. Cardiovascular improvements often take 4-8 weeks to become apparent, while athletic performance enhancements may show within 2-3 weeks.
For maximum therapeutic effect, particularly for circulatory issues or blood pressure management, commit to at least three months of consistent supplementation. Track your progress by noting specific metrics like resting heart rate, exercise endurance, or blood pressure readings. Many users report subtle improvements in energy and circulation during the first few weeks that become more pronounced over time—don’t mistake this gradual progress for ineffectiveness.
Monitor for These Common Side Effects and Solutions
While generally safe, improper arginine supplementation can cause uncomfortable side effects you should know how to manage. Digestive issues like bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort affect approximately 20% of new users, typically when starting higher doses. Prevent these by beginning with 3 grams daily and taking doses with food rather than on an empty stomach.
If digestive problems persist after two weeks, try reducing your dose by 1-2 grams daily then gradually rebuilding. Some users find better tolerance with arginine alpha-ketoglutarate (AAKG) formulations rather than pure L-arginine. More serious reactions like severe gastrointestinal distress, low blood pressure symptoms (dizziness, fainting), or allergic reactions require immediate discontinuation and medical consultation. Never ignore persistent side effects—they indicate your current approach isn’t right for your body.
Avoid These Dangerous Medication Interactions
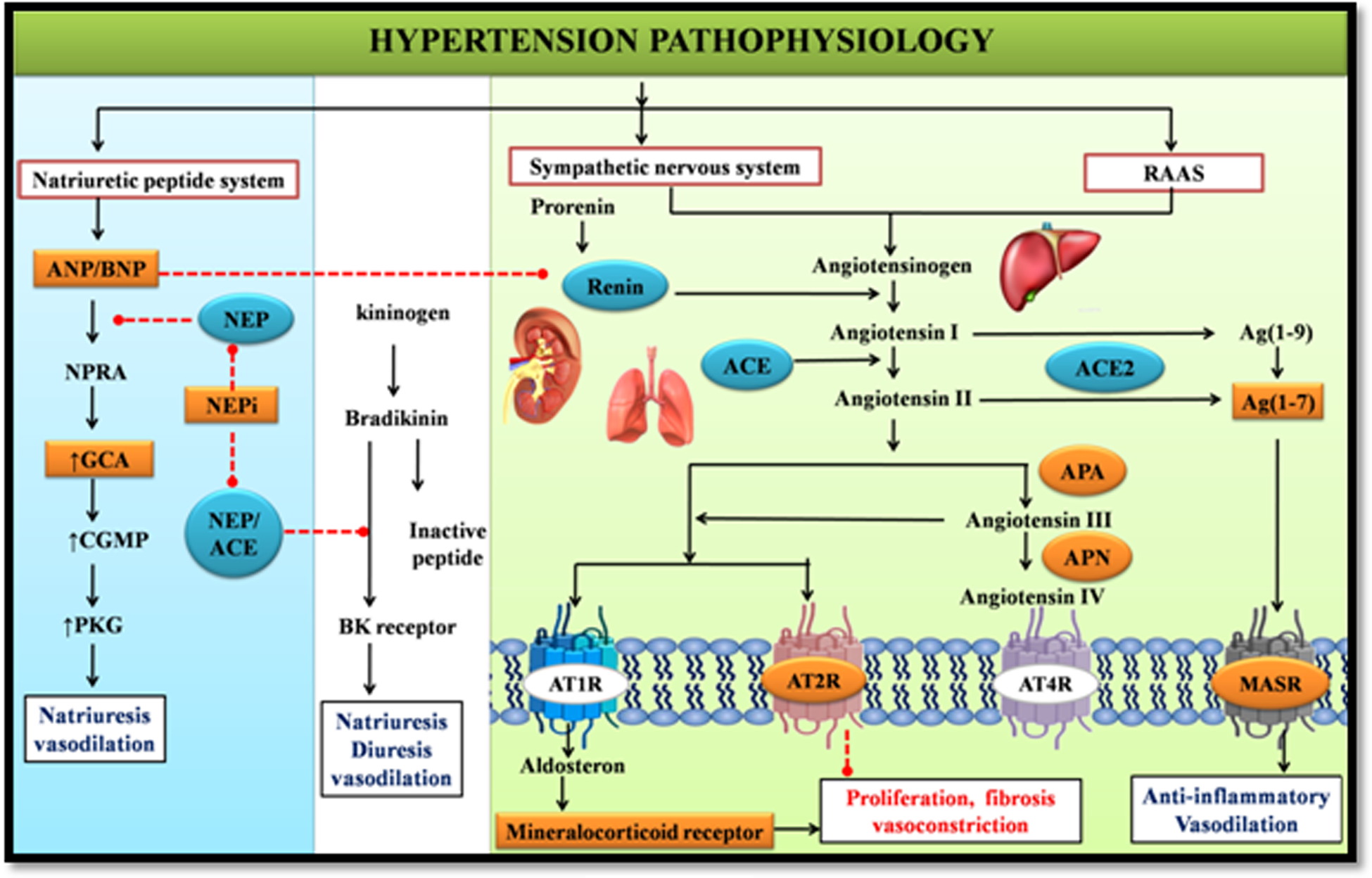
One critical aspect of how to take arginine supplement safely involves understanding dangerous medication interactions. L-arginine significantly interacts with blood pressure medications including:
- ACE inhibitors (benazepril, enalapril, lisinopril)
- ARBs (candesartan, irbesartan, losartan, valsartan)
- Beta-blockers (atenolol, carvedilol, metoprolol)
- Calcium channel blockers (amlodipine, diltiazem, verapamil)
The amino acid’s effect on nitric oxide production can dangerously amplify these medications’ blood pressure-lowering effects. Similarly, arginine interacts with nitrates (nitroglycerin, isosorbide) used for chest pain, potentially causing severe hypotension. Never take arginine supplements if you’re on these medications without explicit approval from your prescribing physician who understands your complete medication profile.
Special Considerations for At-Risk Groups

Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should avoid arginine supplementation unless specifically prescribed and monitored by their obstetrician. Current research hasn’t established safety for developing fetuses or nursing infants, and potential risks outweigh unproven benefits. Those recovering from heart attacks require medical clearance before using arginine, as its vascular effects could interfere with recovery processes.
Individuals with herpes virus (cold sores, genital herpes) should exercise caution—arginine may trigger outbreaks in susceptible people. Always disclose your complete health history to your healthcare provider before starting, especially if you have kidney disease, low blood pressure, or upcoming surgery scheduled. These conditions require personalized medical assessment to determine whether arginine supplementation is appropriate.
Implement These Safety Protocols Before Starting
Before taking your first dose, complete these critical safety steps: First, compile a complete list of all medications, vitamins, and supplements you currently take. Second, schedule a consultation with your healthcare provider to review potential interactions and determine appropriate dosing for your specific health profile. Third, purchase supplements from reputable manufacturers with third-party testing verification.
When beginning supplementation, start with the lowest effective dose and maintain a symptom journal tracking any changes in your health status or side effects. Set reminders to take your doses consistently at the same times each day—missing doses disrupts the steady blood levels needed for optimal results. Most importantly, never view arginine as a replacement for prescribed medications without explicit direction from your healthcare provider.
Final Note: Properly learning how to take arginine supplement transforms it from just another bottle on your shelf into an effective tool for supporting your health goals. By selecting the right form, calculating your precise dosage, timing doses strategically, monitoring for side effects, and avoiding dangerous interactions, you maximize benefits while minimizing risks. Always prioritize professional medical guidance over online advice—your unique health profile requires personalized recommendations that only your healthcare provider can deliver. With the right approach, arginine supplementation can become a valuable component of your wellness routine when used correctly and safely.