Staring at a list of unfamiliar chemical names on your iron supplement bottle? You’re not alone. Most people don’t realize that understanding iron supplement ingredients is crucial for selecting the right product for their specific needs. Knowing what’s inside helps you avoid digestive discomfort, maximize absorption, and ensure you’re getting the elemental iron your body actually requires. This guide breaks down exactly what comprises these essential supplements—both the active iron compounds that treat deficiency and the inactive ingredients that affect tolerability and effectiveness.
Iron deficiency affects millions globally, yet many struggle with supplements due to confusion about ingredients. The average adult body contains just 3-4 grams of iron, yet this tiny amount powers oxygen transport through hemoglobin and supports vital cellular functions. When dietary changes aren’t enough, supplements become necessary—but choosing the right one requires understanding what’s in the bottle. This article reveals how to decode ingredient lists, identify quality formulations, and select supplements that align with your health goals and dietary restrictions.
Ferrous Sulfate vs. Alternative Iron Compounds Explained

When comparing iron supplement ingredients, the active compound determines effectiveness and tolerability more than any other factor. Ferrous sulfate remains the most prescribed form, delivering approximately 20% elemental iron by weight. A standard 325 mg ferrous sulfate tablet provides 65 mg of actual iron—the amount proven effective for treating deficiency. This form works because your intestinal cells are designed to absorb iron in the ferrous (Fe²⁺) state rather than the ferric (Fe³⁺) form found in some supplements.
Why Ferrous Fumarate and Bisglycinate Are Gaining Popularity
Ferrous fumarate delivers about 33% elemental iron, meaning less tablet bulk for the same iron dose—but this concentration often increases digestive side effects. Ferrous bisglycinate chelates iron with glycine, creating a compound that some studies suggest causes fewer gastrointestinal issues and absorbs well even with food. This makes it ideal for sensitive individuals who can’t tolerate standard ferrous sulfate. Carbonyl iron offers a different approach, using microscopic metallic iron particles that release gradually during digestion, potentially reducing stomach upset.
Choosing the Right Active Ingredient for Your Needs
If you experience constipation or nausea with standard supplements, ferrous bisglycinate may provide relief without sacrificing effectiveness. Pregnant women often benefit from gentle formulations due to heightened digestive sensitivity. Always verify the elemental iron content—this number, not the total tablet weight, determines your actual dose. For example, “Iron (as Ferrous Sulfate) 65 mg” means you’re getting 65 mg of usable iron from a larger tablet.
The Critical Difference Between Total Weight and Elemental Iron
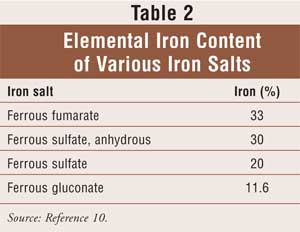
Most confusion about iron supplement ingredients stems from misunderstanding elemental iron content. The 325 mg printed on ferrous sulfate bottles refers to the total compound weight, not the actual iron you absorb. Only 65 mg (20%) represents elemental iron—the amount your body can use. Ferrous fumarate delivers more elemental iron per milligram (33%), while ferrous gluconate provides only 12%.
How to Accurately Compare Supplement Labels
When evaluating products, look for phrases like “Iron (as Ferrous Sulfate) 65 mg” rather than just “Ferrous Sulfate 325 mg.” Quality manufacturers prominently display the elemental iron amount because this determines therapeutic value. Two 325 mg tablets could deliver vastly different iron doses depending on the compound used. Nature Made clearly labels “Iron 65 mg (as Ferrous Sulfate)” so you know exactly what you’re getting.
Why Elemental Iron Percentage Matters for Dosage
Your healthcare provider prescribes based on elemental iron requirements. Taking double the dose of a lower-percentage compound won’t compensate for reduced bioavailability. If you need 65 mg of elemental iron daily, a ferrous sulfate tablet delivers this in one dose, while you’d need nearly three times as much ferrous gluconate to achieve the same result. This knowledge prevents underdosing and unnecessary side effects.
Inactive Ingredients That Make or Break Your Experience

While active ingredients treat deficiency, inactive components determine whether you’ll actually stick with your regimen. These often-overlooked iron supplement ingredients serve critical manufacturing and functional purposes that affect everything from tablet stability to digestive tolerance.
Binders and Disintegrants: The Unsung Heroes
Cellulose gel binds ingredients together while providing structural integrity. Dibasic calcium phosphate adds necessary bulk and stabilizes the tablet. Croscarmellose sodium acts as a disintegrant, ensuring the tablet breaks apart properly in your digestive tract so iron releases efficiently. Without these, supplements wouldn’t dissolve correctly or deliver their active ingredients.
Coatings and Lubricants: Hidden Impact on Tolerance
Hypromellose (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) creates protective coatings that control release timing and improve swallowability. Magnesium stearate prevents ingredients from sticking to manufacturing equipment—a tiny amount that doesn’t affect absorption as some fear. Polysorbate 80 serves as an emulsifier that helps distribute iron evenly and may improve bioavailability. High-quality supplements like Nature Made use natural color sources rather than synthetic dyes, addressing consumer demand for cleaner formulations.
Iron Supplement Ingredients for Special Dietary Needs
Your dietary restrictions should guide your supplement selection as much as your iron needs. Understanding ingredient labels helps you avoid problematic components while ensuring effective treatment.
Gluten-Free and Allergen-Conscious Formulations
Look for explicit “gluten-free” certifications if you have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Reputable brands like Nature Made clearly label gluten-free status since cross-contamination in manufacturing can affect sensitive individuals. Check for allergen statements regarding soy, dairy, or other potential triggers—many quality supplements avoid common allergens entirely.
Vegan and Vegetarian-Friendly Options
Standard gelatin capsules aren’t suitable for plant-based diets. Seek products using cellulose-based capsules instead. Some iron supplements contain animal-derived ingredients in unexpected places—like magnesium stearate sourced from animal fat. Vegan-certified supplements specify plant-derived inactive ingredients throughout. Ferrous bisglycinate often works well for vegetarians since they require 1.8 times more iron due to lower nonheme iron absorption.
Safety Considerations Hidden in the Ingredients List

Certain iron supplement ingredients pose risks that many consumers overlook. Understanding these helps prevent dangerous situations, especially in households with children.
The Critical Child Safety Warning You Must Know
Iron supplements remain a leading cause of fatal poisoning in children under six. The appealing small size and color of tablets make them particularly dangerous. Always store supplements in child-proof containers, preferably locked away. If accidental ingestion occurs, contact poison control immediately—don’t wait for symptoms. Quality manufacturers include prominent child safety warnings on packaging.
Medication Interactions to Discuss with Your Doctor
Magnesium stearate and certain fillers may interact with thyroid medications, antibiotics, and osteoporosis drugs. Discuss all supplements with your healthcare provider, especially if taking prescription medications. Separate iron doses from medications by at least two hours to minimize interactions. Some specialty formulations contain additional ingredients that could complicate medication regimens.
Maximizing Absorption Through Ingredient Awareness
How iron supplement ingredients interact with food and other nutrients dramatically affects their effectiveness. Strategic timing can double your iron absorption.
Vitamin C: Your Secret Absorption Booster
Taking supplements with vitamin C-rich foods like orange juice can triple iron absorption by converting ferric iron to the more absorbable ferrous form. Many quality supplements include ascorbic acid in their ingredient lists specifically for this purpose. If yours doesn’t, take your dose with a glass of orange juice or a vitamin C supplement.
Ingredients to Avoid with Your Iron Dose
Calcium phosphate (a common filler) and dietary calcium compete with iron for absorption. Avoid taking iron supplements within two hours of dairy products, calcium supplements, or antacids. Similarly, coffee, tea, and high-fiber foods inhibit absorption—schedule these separately from your iron dose. Quality supplements minimize absorption-inhibiting ingredients in their formulations.
Recognizing Quality Iron Supplement Ingredients
With minimal FDA oversight, identifying quality supplements requires careful label examination. The right iron supplement ingredients indicate a manufacturer committed to transparency and efficacy.
Third-Party Testing: Your Quality Assurance
Look for USP, NSF, or ConsumerLab verification seals indicating independent testing for purity and label accuracy. Nature Made products consistently earn pharmacist recommendations due to their third-party tested quality. These certifications verify that what’s listed matches what’s inside—critical when dealing with potentially harmful ingredients.
What Reputable Brands Disclose About Their Formulations
Top manufacturers transparently list all ingredients without proprietary blends hiding quantities. They specify iron forms (ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, not just “iron”), use natural colors, and avoid unnecessary additives. Nature Made’s complete ingredient disclosure—including cellulose gel, croscarmellose sodium, and plant-derived colors—exemplifies this transparency. Avoid products with vague terms like “other ingredients” or undisclosed proprietary blends.
When to Consult Your Doctor About Supplement Ingredients
Certain ingredient combinations or reactions warrant professional guidance. Your healthcare provider can help navigate complex situations where standard supplements may not suffice.
Red Flags in Iron Supplement Ingredients
Avoid products containing unverified “proprietary blends” or excessive fillers with no stated purpose. Steer clear of supplements with artificial colors like Red 40 or Yellow 5 if you have sensitivities. If you notice unexpected side effects like severe constipation or allergic reactions, review the inactive ingredients with your doctor—they may pinpoint the culprit.
Special Considerations for Chronic Health Conditions
If you have inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, or have had gastric bypass surgery, standard iron supplement ingredients may not work for you. Your healthcare provider might recommend specialized formulations like SiderAL Forte that use different delivery systems. Always disclose all health conditions before starting supplementation—some ingredients could worsen underlying issues.
Understanding iron supplement ingredients transforms confusing label reading into empowered decision-making. The active iron compound determines therapeutic value, while inactive ingredients significantly impact tolerability and adherence. Always verify elemental iron content rather than total tablet weight, look for third-party testing certifications, and consider your dietary restrictions when selecting products. Proper administration—taking supplements on an empty stomach with vitamin C while avoiding absorption inhibitors—maximizes benefits. Most importantly, store iron supplements securely away from children and consult your healthcare provider about potential medication interactions. With this knowledge, you can confidently select supplements that effectively address deficiency while minimizing side effects—getting the iron your body needs without compromising your comfort or safety.