You’ve probably heard about omega-3s, but do you know why these essential fatty acids could be the missing piece in your health routine? The benefits of omega 3 supplementation extend far beyond basic nutrition—these powerful compounds play critical roles in brain function, heart health, and inflammation control. With most people falling short of optimal intake through diet alone, understanding how omega-3 supplements can transform your health is more important than ever.
Unlike other fats, your body can’t produce omega-3 fatty acids on its own, making dietary intake or supplementation essential for maintaining critical bodily functions. These compounds serve as fundamental building blocks for cell membranes throughout your body and act as precursors for signaling molecules that influence everything from cognitive performance to cardiovascular function. Decades of research confirm that adequate omega-3 levels—whether from fish, plant sources, or high-quality supplements—support optimal health at every stage of life.
This guide cuts through the confusion to deliver science-backed insights on how omega-3 supplementation specifically enhances cognitive function, protects heart health, and regulates inflammation. You’ll discover which forms deliver the most significant benefits, how to determine your ideal dosage, and why certain populations experience more dramatic improvements than others.
How EPA and DHA Outperform ALA for Health Benefits

When selecting an omega-3 supplement, understanding the differences between alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is crucial for maximizing health outcomes. While ALA from plant sources like flaxseed and chia seeds serves as an essential starting point, EPA and DHA deliver the most significant health benefits due to their direct physiological effects.
Why Your Body Needs Direct EPA and DHA Intake
The conversion process from ALA to EPA and DHA is remarkably inefficient—less than 15% of consumed ALA transforms into EPA, and less than 5% converts to DHA. This biological limitation means that relying solely on plant-based sources won’t provide sufficient levels of these critical long-chain omega-3s. Marine sources like fatty fish, fish oil, and krill oil deliver EPA and DHA directly, bypassing this inefficient conversion process.
Your brain contains approximately 50-60% lipids by weight, with DHA accounting for more than 40% of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in neural tissue. This high concentration isn’t accidental—it reflects DHA’s essential role in maintaining the structural integrity of brain cells and supporting optimal neurotransmission. Similarly, your retina depends on DHA for proper light-sensing function in photoreceptor cells.
Which Omega-3 Form Delivers Maximum Cognitive Benefits?
Research comparing EPA-rich versus DHA-rich supplements reveals distinct cognitive effects:
- EPA-rich supplementation reduces activity in the anterior cingulate cortex while increasing activity in the right precentral gyrus, leading to faster response times on cognitive tasks
- DHA supplementation enhances activity in the right precentral gyrus during spatial cognition tasks
- Krill oil (rich in phospholipid-bound omega-3s) shows particularly strong effects on frontal brain regions compared to other sources
This evidence suggests EPA may be more effective than DHA for improving certain aspects of neurocognitive function over shorter supplementation periods of one month or more.
Boost Memory and Learning with Targeted Omega-3 Dosing
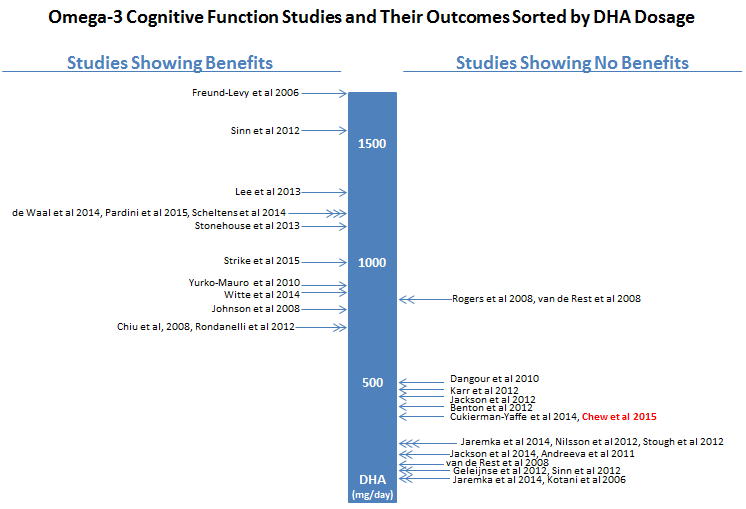
Clinical evidence demonstrates that strategic omega-3 supplementation can significantly enhance cognitive performance, particularly for learning and memory. However, not all approaches deliver equal results—specific dosing protocols and duration are critical for achieving measurable improvements.
Proven Dosage Protocols for Cognitive Enhancement
Research identifies these effective supplementation strategies:
- 900 mg of DHA daily for 24 weeks substantially reduces errors on learning and memory tests, with serum DHA levels quadrupling in participants
- 2.2 grams of combined EPA/DHA daily for 26 weeks improves executive functions by 26% in adults aged 50-75
- 1-2 grams of fish oil daily increases cerebral blood flow during cognitive tasks, with the 2-gram dose producing significantly higher oxyhemoglobin levels
Critical timing factor: Most studies show cognitive benefits emerge after 12-24 weeks of consistent supplementation. Shorter durations typically fail to produce significant improvements.
Who Benefits Most from Omega-3 Cognitive Support?
Certain populations experience more pronounced cognitive improvements from omega-3 supplementation:
- Older adults with existing cognitive concerns
- Individuals with low baseline omega-3 status (especially below 4% on the omega-3 index)
- People experiencing social isolation or loneliness (omega-3s at 1.25-2.5 grams daily mitigate loneliness-related cognitive decline)
- Those with the APOE4 gene variant (which increases Alzheimer’s risk)
If you fall into one of these categories, omega-3 supplementation may deliver particularly significant cognitive protection.
Reduce Heart Disease Risk with Omega-3 Cardiovascular Protection
The cardiovascular benefits of omega-3 supplementation represent some of the most well-documented effects, with mechanisms extending far beyond simple triglyceride reduction. Understanding how EPA and DHA protect your heart can help you maximize these life-saving benefits.
3 Key Heart-Protective Mechanisms of Omega-3s
-
Inflammation regulation: Omega-3s shift eicosanoid production toward less inflammatory mediators, reducing chronic vascular inflammation that drives atherosclerosis development
-
Heart rate modulation: DHA consumption produces substantial reductions in resting heart rate, potentially lowering risk of catastrophic cardiac events
-
Blood pressure support: The FDA recognizes that omega-3 consumption may lower risk of high blood pressure through multiple physiological pathways
Unlike statins that primarily target cholesterol, omega-3s work through complementary mechanisms that address different aspects of cardiovascular health.
Optimal Omega-3 Intake for Heart Health
For meaningful cardiovascular protection:
- Maintain an omega-3 index (EPA+DHA in erythrocyte membranes) of at least 8%
- Consume 1-2 grams of EPA/DHA daily from supplements if dietary intake is insufficient
- Combine supplementation with fatty fish consumption (2-3 servings weekly of salmon, mackerel, or sardines)
Western populations typically show erythrocyte EPA and DHA levels of 3-5%, while Japanese populations with high fish consumption demonstrate levels approximately twice as high—correlating with their significantly lower cardiovascular disease rates.
Combat Chronic Inflammation with Omega-3 Resolution Pathways
The anti-inflammatory benefits of omega-3 supplementation extend beyond simple suppression—they actively promote inflammation resolution through specialized biological pathways that many people don’t understand.
How Omega-3s Resolve Inflammation (Not Just Suppress It)
While omega-6 fatty acids promote inflammatory eicosanoids, EPA serves as a precursor for specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) that actively guide your body through the resolution phase of inflammation. This paradigm shift in understanding means omega-3s don’t merely dampen inflammation—they help your body complete the inflammatory process properly, preventing transition to chronic inflammation.
The competition between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids for enzymatic conversion means your dietary ratio significantly impacts inflammatory status. Western diets typically provide omega-6 to omega-3 ratios of 15:1-20:1, while traditional diets maintain ratios around 4:1 or lower. Supplementation with EPA and DHA can help restore a more favorable inflammatory profile even when dietary patterns remain unchanged.
Determine Your Ideal Omega-3 Dosage and Duration
Finding your optimal omega-3 supplementation protocol requires understanding both general guidelines and your personal factors that influence response. The “one-size-fits-all” approach fails to deliver maximum benefits for most people.
Daily Intake Guidelines by Life Stage
| Age Group | Male (g/day) | Female (g/day) | Pregnancy (g/day) | Lactation (g/day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-6 mo | 0.5 | 0.5 | — | — |
| 7-12 mo | 0.5 | 0.5 | — | — |
| 1-3 yrs | 0.7 | 0.7 | — | — |
| 4-8 yrs | 0.9 | 0.9 | — | — |
| 9-13 yrs | 1.2 | 1.0 | — | — |
| 14-50 yrs | 1.6 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.3 |
| 51+ yrs | 1.6 | 1.1 | — | — |
Important safety limit: The FDA recommends no more than 3 grams of omega-3 daily from all sources, with supplements providing no more than 2 grams. Higher doses may increase bleeding risk, especially when combined with anticoagulant medications.
4 Factors That Determine Your Optimal Dosage
- Baseline omega-3 status: Those with low levels (omega-3 index <4%) typically need higher initial doses
- Age: Individuals under 60 often show greater serum response to supplementation than those over 60
- Genetic factors: APOE4 carriers may process DHA differently, requiring adjusted protocols
- Health goals: Cognitive support typically requires 900mg-2.5g daily, while cardiovascular protection may need 1-2g
If you take blood thinners or have bleeding disorders, consult your healthcare provider before starting omega-3 supplementation. For most people, side effects like fishy aftertaste or mild gastrointestinal discomfort can be minimized by taking supplements with meals or choosing enteric-coated formulations.
Assess Your Omega-3 Status Before Supplementing
Knowing your current omega-3 status transforms supplementation from guesswork into a precision health strategy. Two primary testing methods provide valuable insights:
Erythrocyte Omega-3 Index vs. Plasma Measurement
- Erythrocyte (red blood cell) test: Reflects intake over the past 120 days; the gold standard for assessing long-term status
- Below 4%: High cardiovascular risk
- 4-8%: Intermediate risk
-
8% or higher: Low cardiovascular risk
-
Plasma/serum phospholipid test: Reflects recent intake (days to weeks)
- Average Western levels: 3-4% EPA+DHA
- Japanese population levels: Approximately 8% (correlating with lower heart disease rates)
Without testing, you’re supplementing blind—potentially taking too little for meaningful benefits or more than necessary. Consider an omega-3 index test before starting supplementation, then retest after 4-6 months to assess effectiveness.
Maximize Omega-3 Absorption with Proper Supplement Selection
Not all omega-3 supplements deliver equal benefits due to differences in absorption and bioavailability. Understanding these factors helps you select products that deliver maximum value.
Triglyceride vs. Ethyl Ester vs. Phospholipid Forms
- Triglyceride form: Naturally occurring in fish; excellent absorption
- Ethyl ester form: Common in concentrated supplements; slightly lower absorption
- Phospholipid form (krill oil): May enhance delivery to specific tissues like the brain
While absorption rates for all forms exceed 95%, the molecular structure influences how omega-3s are distributed to different tissues. For cognitive benefits, phospholipid-bound forms may offer advantages due to their structural similarity to brain cell membranes.
Pro tip: Take omega-3 supplements with a fat-containing meal to maximize absorption—omega-3s are fat-soluble compounds that require dietary fat for optimal uptake.
Final Action Plan for Omega-3 Supplementation Success
To maximize the benefits of omega-3 supplementation, follow this evidence-based approach:
-
Prioritize EPA and DHA over ALA for direct health benefits—aim for supplements providing at least 500mg combined EPA/DHA per serving
-
Commit to 12-24 weeks of consistent supplementation before evaluating cognitive benefits—shorter durations typically yield minimal results
-
Combine supplementation with 2-3 weekly servings of fatty fish for synergistic benefits that extend beyond isolated supplementation
-
Consider testing your omega-3 index if you have cardiovascular concerns or want precision dosing
-
Match dosage to your needs: 1-2 grams daily for general health, up to 2.5 grams for specific cognitive support in at-risk populations
The strongest evidence supports omega-3 supplementation for cognitive enhancement in older adults, cardiovascular protection, and inflammation regulation. By implementing these science-backed strategies, you’ll transform omega-3 supplementation from a generic health habit into a targeted intervention that delivers measurable improvements in brain function, heart health, and overall well-being.




