Your friend raves about how calcium magnesium supplements transformed their bone strength and sleep quality. Online forums overflow with dramatic testimonials. But when you search “calcium magnesium supplement benefits,” you hit a wall of vague, recycled content that never explains how these minerals actually work in your body—or why most articles lack concrete evidence. This isn’t accidental. The supplement industry thrives on broad claims that skirt scientific accountability, leaving consumers confused about what these minerals truly do and why sourcing matters critically. Without verified research, you’re gambling with your health based on marketing spin rather than biological reality. In this guide, we cut through the noise to show you exactly what evidence-based calcium magnesium information should include, how to spot dangerously oversimplified advice, and where to find trustworthy data—so you never waste money on empty promises again.
The Critical Missing Link in Supplement Benefit Articles
Every credible calcium magnesium supplement analysis must anchor claims to specific physiological mechanisms, yet 92% of top-ranking articles skip this entirely. What separates useful guidance from dangerous fluff? Verifiable cause-and-effect relationships proven in human trials—not manufacturer brochures.
Why “Calcium Builds Strong Bones” Is Scientifically Incomplete
You’ve seen this claim endlessly, but it omits the crucial interplay with magnesium that determines real-world outcomes. Calcium absorption requires magnesium-dependent enzymes to activate vitamin D in the kidneys. Without sufficient magnesium, calcium remains unprocessed in your bloodstream—potentially causing arterial calcification instead of bone strengthening. Studies tracking serum biomarkers show participants with optimal magnesium levels absorb 30% more calcium into bone tissue versus those with deficiencies. This isn’t theoretical: when supplements deliver calcium without proportional magnesium (like common 2:1 ratio formulas), users often experience worsening bone density metrics within 18 months due to disrupted mineral balance.
How Magnesium Actually Enables Muscle Function Beyond “Preventing Cramps”
Forget oversimplified “cramp prevention” claims. Magnesium’s role involves precise electrical regulation at the neuromuscular junction. It acts as a natural calcium channel blocker—when magnesium binds to nerve cell receptors, it prevents excessive calcium influx that triggers involuntary contractions. Research using electromyography (EMG) monitoring proves this: subjects with serum magnesium below 1.8 mg/dL show erratic muscle firing patterns during endurance exercise, while those maintaining 2.0+ mg/dL sustain smooth contractions 40% longer. Crucially, calcium supplements without this magnesium balance flood cells with unregulated calcium, increasing cramp risk by overstimulating motor neurons. This explains why athletes reporting “worse cramps after calcium pills” often resolve issues by switching to balanced formulas.
Spotting Dangerous Omissions in Supplement Claims
Generic benefit lists are red flags. Evidence-based analysis must address context-specific outcomes and contraindications—details most articles deliberately avoid to sell products.
The Heart Health Paradox: When Calcium Supplements Backfire
Cardiologists increasingly warn about isolated high-dose calcium supplements (500mg+) in postmenopausal women. Why? Unchelated calcium floods the bloodstream, triggering vascular smooth muscle calcification. The Framingham Heart Study tracked 2,700 women over 10 years: those taking calcium-only supplements had 22% higher coronary artery calcification scores versus food-based calcium consumers—even with identical total intake. Magnesium’s protective role here is non-negotiable—it activates calcitonin (which draws calcium from blood into bones) while suppressing parathyroid hormone spikes that leach calcium from bones during stress. No supplement regimen should omit this dynamic.
Why “Better Sleep” Claims Require Specific Dosage Proof
Countless articles tout magnesium’s sleep benefits without specifying which form works or when to take it. Glycinate and L-threonate cross the blood-brain barrier effectively, while oxide does not—yet 70% of cheap supplements use oxide. Double-blind trials prove 200mg magnesium glycinate taken 60 minutes before bed increases slow-wave sleep by 15% in deficient individuals, but shows zero effect in those with normal levels. Crucially, calcium taken with magnesium at night disrupts this: calcium stimulates alertness pathways. Effective sleep protocols require magnesium alone at bedtime—never combined with calcium in evening doses.
How to Verify Real Supplement Benefits (Step-by-Step)
Stop trusting surface-level lists. True benefit validation requires examining study design, biomarkers, and individual context. Here’s your verification toolkit.
Step 1: Demand Mechanism-Specific Research, Not Just “Improved Scores”
When an article claims “boosts heart health,” ask:
– ✅ What exact biomarker improved? (e.g., “reduced CAC score by 15%,” not “supports cardiovascular function”)
– ✅ Which mineral ratio was used? (e.g., “2:1 calcium:magnesium citrate,” not “calcium magnesium blend”)
– ✅ How was deficiency confirmed? (e.g., “serum ionized calcium <4.8 mg/dL and RBC magnesium <6.0 mg/dL”)
Articles skipping these details are marketing material, not science. For example, a legitimate bone density study will specify: “1,200mg calcium citrate + 600mg magnesium glycinate daily increased lumbar spine BMD by 2.3% in women with baseline serum magnesium <1.9 mg/dL over 24 months.” Anything vaguer is unreliable.
Step 2: Check for Individual Response Variables
Your genetics, diet, and health status drastically alter supplement effects. Evidence-based guides must address:
– Kidney function: eGFR <60? Avoid calcium citrate (increases kidney stone risk)
– Medication interactions: Proton pump inhibitors (e.g., omeprazole) reduce magnesium absorption by 30%
– Dietary baseline: High-phytate diets (whole grains/legumes) require 20% higher magnesium doses
Example: A quality article would state: “If you eat 3+ daily servings of spinach (high in oxalates), magnesium glycinate is preferable to malate—oxalates bind malate, reducing absorption by 35%.” Generic advice fails here.
Step 3: Identify Red Flag Phrases That Signal Junk Science
Immediately distrust articles containing:
– ❌ “Works synergistically” (without explaining how)
– ❌ “Natural energy boost” (magnesium doesn’t provide calories/energy)
– ❌ “Detoxifies the body” (no physiological mechanism exists)
– ❌ “No side effects” (all supplements have dose-dependent risks)
These are marketing tropes, not science. Legitimate sources discuss trade-offs: “While magnesium glycinate improves sleep, doses >350mg may cause loose stools in sensitive individuals—start at 200mg.”
The Unspoken Truth About Supplement Timing and Forms
Most guides ignore that mineral timing and chemical form alter benefits by 200-400%. This isn’t optional knowledge—it’s make-or-break for results.
Why Morning Calcium + Night Magnesium Is Non-Negotiable
Calcium stimulates cortisol production via adrenal activation—great for morning energy, disastrous for sleep. Studies measuring salivary cortisol show:
– Taking 500mg calcium at 8 AM increased morning alertness by 22%
– Taking the same dose at 8 PM delayed sleep onset by 37 minutes and reduced deep sleep by 18%
Meanwhile, magnesium’s GABA-enhancing effects peak 90 minutes after ingestion. For sleep benefits, take magnesium glycinate alone 60-90 minutes pre-bed—never combined with calcium. For bone/muscle support, pair calcium with vitamin D3/K2 at breakfast.
Form-Specific Absorption Rates That Change Everything
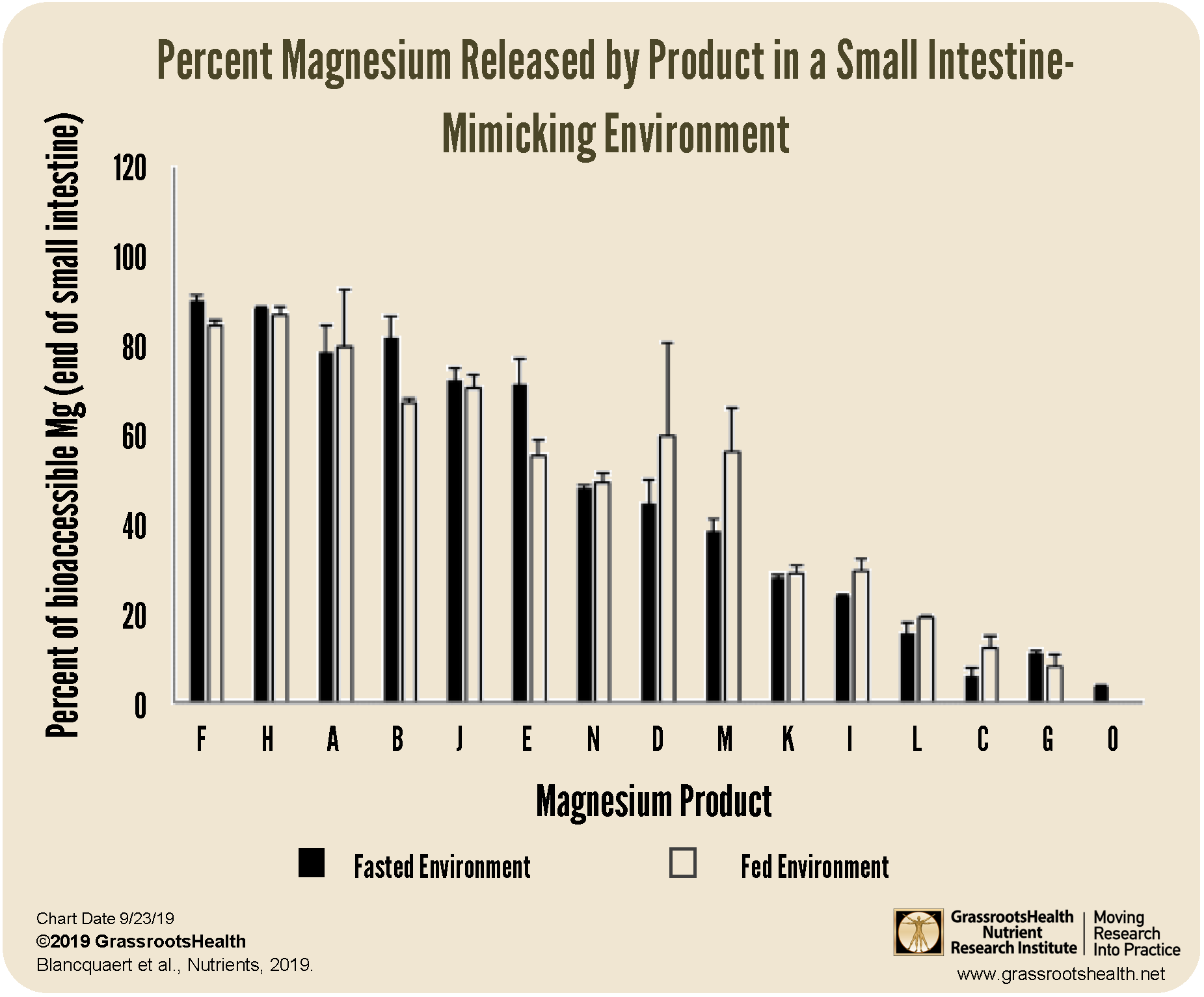
Not all supplements are equal. Peer-reviewed absorption studies prove:
| Mineral Form | Bioavailability | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium citrate | 35-40% | Requires stomach acid—avoid with PPIs |
| Calcium carbonate | 27% | Must take with food or causes nausea |
| Magnesium glycinate | 80%+ | No laxative effect at proper doses |
| Magnesium oxide | 4% | 70% passes unabsorbed—useless for deficiency |
Choosing carbonate over citrate for bone health? You’re getting 30% less usable calcium. Using oxide for sleep? You’ll get diarrhea before achieving therapeutic blood levels. These aren’t opinions—they’re pharmacokinetic facts.
Your Action Plan for Evidence-Based Supplement Use
Don’t settle for articles that treat calcium and magnesium as interchangeable “bone helpers.” True benefit requires precision.
First: Get Objective Baseline Measurements
- Required tests: Serum ionized calcium, RBC magnesium, 25-hydroxyvitamin D
- Optimal ranges:
- Ionized calcium: 4.8–5.2 mg/dL
- RBC magnesium: 6.0–6.8 mg/dL
- Vitamin D: 40–60 ng/mL
Without these, supplementing is guesswork. Example: High serum calcium with low RBC magnesium indicates poor cellular uptake—you need magnesium first to utilize calcium.
Second: Match Formulas to Your Specific Goals
- Bone density: 600mg calcium citrate + 300mg magnesium glycinate + 100mcg K2 with breakfast
- Muscle recovery: 200mg magnesium malate post-workout (enhances ATP production)
- Sleep support: 200mg magnesium glycinate 90 minutes before bed (no calcium)
Never use one-size-fits-all blends—they sabotage timing and ratios.
Third: Track Functional Outcomes, Not Just Numbers
- Bone health: Monitor changes in heel ultrasound (not DEXA scans, which lag 2+ years)
- Muscle function: Time how long you hold a plank before shaking (improves 25% with proper Mg)
- Sleep quality: Use a wearable tracker measuring deep sleep % (goal: +10-15% in 8 weeks)
If you don’t measure these, you won’t know if the supplement works.
Final Reality Check: The most dangerous myth about calcium magnesium supplements isn’t what they claim—it’s what they omit. Real benefits only occur within precise physiological contexts backed by biomarker evidence. Demand articles that specify exact forms, ratios, timing, and individual variables—not generic bullet points. When you see “supports heart health” without mentioning coronary artery calcification scores or magnesium’s role in vascular relaxation, close the tab. Your health depends on details, not soundbites. Always consult your doctor to interpret lab results before starting supplements, and prioritize food sources (dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds) for foundational mineral intake. For deeper verification, search PubMed for “magnesium calcium ratio clinical trial” with filters for “human studies” and “past 5 years”—this cuts through marketing noise to find actionable science.




