You’ve likely heard about hawthorn berry’s heart-healthy benefits, but understanding hawthorn berry supplement side effects is crucial before adding this traditional remedy to your routine. Derived from the Crataegus plant, these supplements have been used for centuries in both Chinese and European medicine, primarily for cardiovascular support. While generally well-tolerated, hawthorn’s active compounds can interact with your body in ways that cause unintended reactions—especially if you take medications or have underlying health conditions. This guide cuts through the confusion to give you precise, evidence-based information about potential risks so you can make informed decisions about your health.
Unlike many herbal supplements that lack thorough safety research, hawthorn has been studied extensively for heart conditions. Yet incomplete safety data for certain populations means you shouldn’t assume it’s risk-free. By the end of this article, you’ll know exactly which side effects to watch for, dangerous medication combinations to avoid, and practical steps to use hawthorn safely under proper medical guidance.
Why Your Heart Might React to Hawthorn Supplements
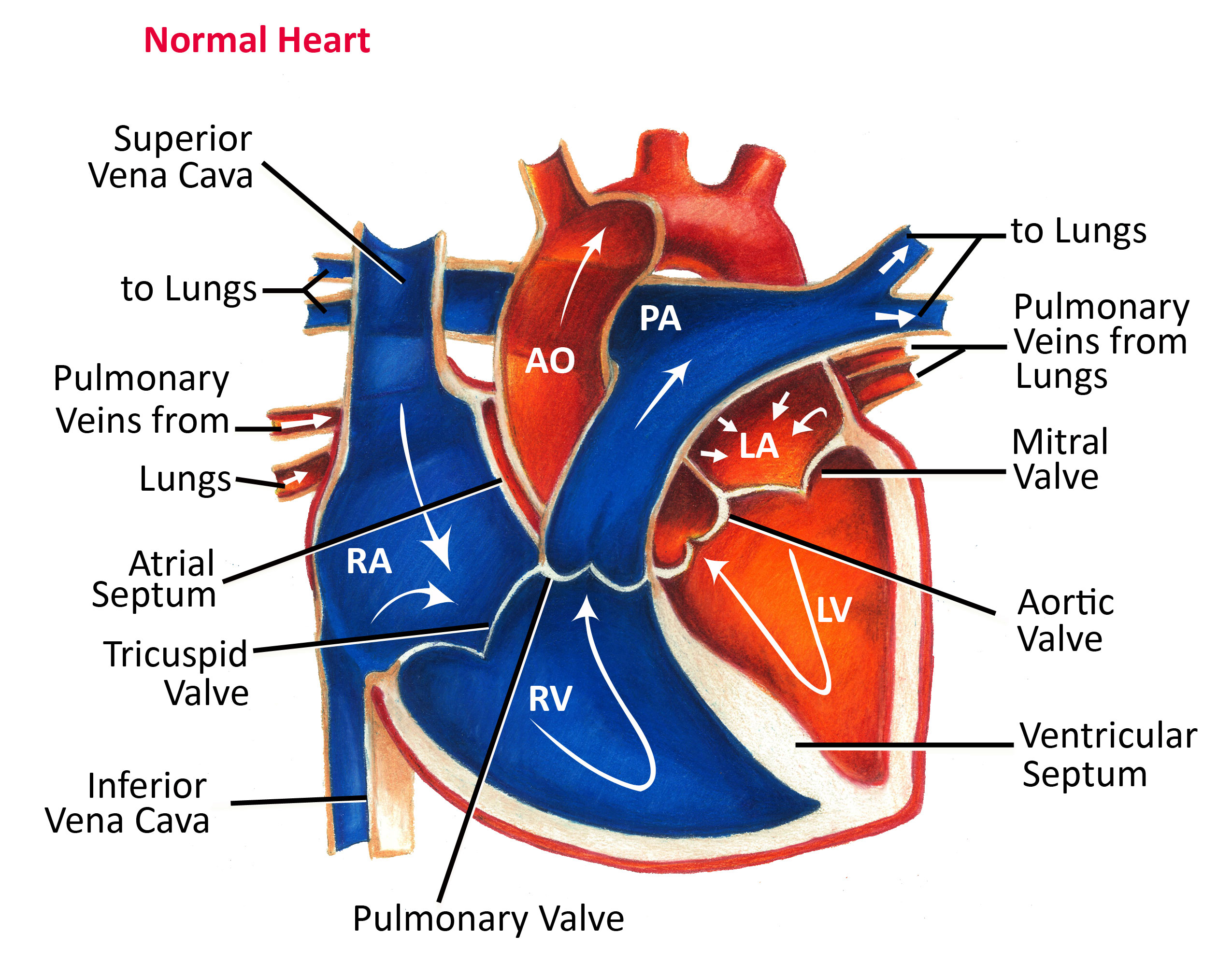
Hawthorn’s cardiovascular activity explains why most side effects manifest in heart function or blood pressure regulation. The plant’s flavonoids inhibit 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase, which increases heart rate and produces positive inotropic effects—essentially strengthening heart contractions. While beneficial for some heart conditions, this mechanism means your cardiovascular system bears the brunt of any adverse reactions. Understanding this connection helps you recognize whether symptoms relate to hawthorn or other health issues.
Most clinical studies report good tolerability, with side effects typically mild and reversible upon discontinuation. However, one smaller trial suggested an increased early risk of disease progression in heart failure patients, highlighting why medical supervision matters even with “natural” supplements. The Cochrane Collaboration’s review of hawthorn for chronic heart failure noted the need for additional research but didn’t identify major safety concerns when used appropriately under supervision.
Your individual response depends on multiple factors including dosage, supplement quality, and your unique physiology. Starting with lower doses allows your body to adjust gradually while helping you identify any sensitivity before escalating to therapeutic levels recommended for specific conditions.
Mild Reactions You Might Experience Daily
Over 80% of hawthorn users report no significant issues, but some experience manageable side effects that typically resolve within days. These common reactions include:
- Digestive discomfort: Nausea, stomach upset, or diarrhea when first starting supplementation
- Cardiovascular adjustments: Mild dizziness or temporary palpitations as your circulation adapts
- Subtle neurological effects: Occasional headaches or fatigue during initial use
These symptoms often diminish as your body adjusts to the supplement, usually within one to two weeks. If gastrointestinal issues persist beyond this adjustment period, consider taking hawthorn with food or reducing your dose—never ignore ongoing digestive distress as it may indicate hawthorn isn’t compatible with your system.
The vasodilatory effects responsible for hawthorn’s blood pressure benefits can cause temporary lightheadedness, especially when standing quickly. Combat this by rising slowly from seated positions and ensuring adequate hydration. Track your symptoms in a journal to identify patterns and share this information with your healthcare provider during follow-up appointments.
Dangerous Drug Combinations You Must Avoid
Blood Thinners That Could Cause Uncontrolled Bleeding
Hawthorn significantly increases bleeding risk when combined with anticoagulants like warfarin or antiplatelet medications including aspirin and clopidogrel. Laboratory studies confirm hawthorn enhances these medications’ effects through multiple mechanisms, though clinical relevance in humans requires more research. The theoretical risk is serious enough that you should never combine these treatments without explicit medical approval and monitoring.
Signs of dangerous bleeding include:
– Unusual bruising that appears without injury
– Prolonged bleeding from minor cuts
– Blood in urine or stool
– Heavy menstrual bleeding
If you take any blood-thinning medication—even occasional aspirin—disclose your hawthorn use to your healthcare provider immediately. They’ll likely recommend regular clotting function tests to ensure your INR levels remain within safe parameters while using both treatments.
Digoxin Interactions That Skew Critical Measurements
Patients taking digoxin face a dual risk when using hawthorn supplements. First, hawthorn compounds interfere with laboratory immunoassays used to measure serum digoxin levels, potentially causing dangerously inaccurate results. You might receive inappropriate dose adjustments based on false readings, leading to toxicity or treatment failure. Second, pharmacodynamic interactions mean hawthorn and digoxin affect each other’s cardiovascular activity in unpredictable ways.
This combination requires strict medical supervision with alternative testing methods to monitor digoxin levels accurately. Never start hawthorn if you take digoxin without your cardiologist’s explicit approval and a revised monitoring plan that accounts for this complex interaction.
Who Absolutely Should Skip Hawthorn Supplements

Pregnant Women Facing Unknown Risks
Traditional medicine explicitly prohibits hawthorn use during pregnancy due to insufficient safety data. The lack of comprehensive clinical studies means researchers don’t understand how hawthorn’s cardiovascular effects might impact fetal development or maternal circulation. Women who are pregnant or planning conception should avoid all hawthorn preparations—including berry, leaf, and flower extracts—unless their obstetrician specifically recommends otherwise for a documented medical condition.
Breastfeeding mothers should exercise similar caution since hawthorn compounds could potentially pass into breast milk. Wait until you’ve finished nursing before considering hawthorn supplementation, and discuss alternatives with your healthcare provider that have better-established safety profiles for nursing mothers.
Pre-Surgery Patients Needing Blood Pressure Stability
If you have surgery scheduled within the next two weeks, discontinue hawthorn immediately. Its blood pressure effects and potential interaction with anesthesia medications create unnecessary risks during surgical procedures. Inform your surgical team about all supplements you’ve taken recently, as hawthorn’s effects may linger even after stopping. Most surgeons recommend halting hawthorn at least 14 days preoperatively to ensure stable cardiovascular function during your procedure.
Smart Strategies for Safe Hawthorn Use
Start with 160-300 mg daily of standardized extract (containing 18.75% oligomeric procyanidins) and increase gradually only under medical guidance. This conservative approach helps identify your personal tolerance threshold while minimizing reaction risks. Quality matters significantly—choose supplements with third-party verification from USP, NSF, or ConsumerLab to ensure accurate dosing and absence of contaminants.
Monitor your blood pressure twice daily during the first two weeks of use, especially if you take hypertension medications. Record readings along with dosage information to share with your healthcare provider at follow-up appointments. This data helps determine whether hawthorn complements your treatment plan or requires medication adjustments to prevent excessive blood pressure reduction.
Schedule a follow-up appointment within 30 days of starting hawthorn to review your symptom journal, blood pressure logs, and any concerns. Your provider may order additional tests based on your health profile, such as digoxin levels if you take that medication or clotting studies if you’re on blood thinners. Never view hawthorn as a replacement for prescribed heart medications—its role is strictly complementary under professional supervision.
Warning Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Don’t dismiss these symptoms as normal adjustment effects—they indicate potentially dangerous reactions:
– Chest pain or pressure that radiates to your arm or jaw
– Severe dizziness causing near-fainting or actual loss of consciousness
– Irregular heartbeat accompanied by shortness of breath or fatigue
– Unexplained swelling in your legs, ankles, or abdomen
These could signal worsening heart failure or dangerous interactions with your current medications. Stop taking hawthorn immediately and contact your healthcare provider or seek emergency care if you experience any of these symptoms. Early intervention prevents minor issues from escalating into serious health crises.
Remember that hawthorn’s benefits for heart health come with responsibility—you must remain vigilant about your body’s signals and maintain open communication with your medical team. The goal isn’t to scare you away from potentially beneficial supplementation but to ensure you use hawthorn knowledgeably and safely as part of an integrated heart health strategy.
Hawthorn berry supplements offer genuine cardiovascular benefits but demand respect for their pharmacological activity. The mild side effect profile enjoyed by most users shouldn’t create false confidence—serious interactions with common heart medications require professional oversight. Always disclose hawthorn use to every healthcare provider you see, especially cardiologists and surgeons. By starting low, monitoring closely, and maintaining open communication with your medical team, you can safely determine whether hawthorn belongs in your health regimen. Never let “natural” labeling trick you into skipping the essential step of professional medical consultation before beginning supplementation.




