When Medicare Part A and Part B leave you facing unexpected medical bills, understanding how Medicare supplement works becomes essential for protecting your retirement savings. Original Medicare covers many healthcare services, but it leaves significant gaps that can lead to thousands in out-of-pocket costs each year. If you’ve received a bill showing you’re responsible for 20% coinsurance after a doctor’s visit or faced a $1,600 hospital deductible, you’ve experienced why nearly 15 million Medicare beneficiaries rely on Medigap policies. Learning how Medicare supplement works empowers you to transform unpredictable healthcare expenses into a stable monthly premium you can budget for with confidence.
Medicare Supplement Insurance, officially called Medigap, bridges the financial gaps in Original Medicare by covering costs like copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles. Unlike Medicare Advantage plans that replace Original Medicare, Medigap policies work alongside your existing Part A and Part B coverage to minimize surprise bills. Whether you’re approaching 65 or recently discovered gaps in your Medicare coverage, grasping how Medicare supplement works helps you avoid financial shocks from routine care to major medical events. This guide explains exactly how these supplemental policies function in real-world scenarios so you can determine if Medigap aligns with your healthcare needs and financial planning.
Why Original Medicare Needs Supplemental Coverage

Original Medicare leaves beneficiaries responsible for three major cost categories that can quickly drain savings without supplemental protection. Understanding these coverage gaps reveals exactly how Medicare supplement works to protect your finances when medical care becomes necessary.
Copayments That Add Up With Every Doctor Visit
Each time you see a specialist or primary care physician under Original Medicare, you pay a fixed copayment amount out of pocket. For many beneficiaries managing chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease, these $20-$50 copayments accumulate rapidly with frequent appointments. A single specialist visit might seem manageable, but when you require multiple specialists and regular check-ups, these costs compound throughout the year. Medigap policies eliminate these recurring copayment expenses, ensuring you don’t avoid necessary care due to cost concerns.
Coinsurance That Can Reach Thousands Per Hospital Stay
Medicare’s 80/20 coinsurance structure means the program covers approximately 80% of approved costs for many services, leaving you responsible for the remaining 20%. While this works for routine care, it becomes problematic during hospitalization or major procedures. Consider this real scenario: a three-day hospital stay with $15,000 in Medicare-approved costs would leave you owing $3,000 in coinsurance under Original Medicare alone. Learning how Medicare supplement works shows you that Medigap policies cover this percentage-based responsibility, preventing a single medical event from becoming a financial catastrophe.
Annual Deductibles That Reset Your Out-of-Pocket Counter
Both Medicare Part A and Part B have annual deductibles you must meet before coverage begins. The Part A hospital deductible resets with each benefit period, meaning multiple hospital stays in a year could require paying the deductible multiple times. For 2024, this deductible stands at $1,600 per benefit period—money you must pay entirely out of pocket before Medicare coverage activates. How Medicare supplement works includes covering these deductibles so your coverage begins immediately without waiting to meet financial thresholds.
Qualifying for Medigap Coverage Without Medical Hassles
To benefit from how Medicare supplement works, you must meet specific eligibility requirements that ensure Medigap functions as true supplemental coverage rather than a replacement for Original Medicare.
The Non-Negotiable Enrollment Requirement
You must actively maintain both Medicare Part A and Part B to purchase any Medigap policy. Part A provides your hospital insurance while Part B covers medical services—both components work together as the foundation that Medigap builds upon. This dual-enrollment requirement exists because Medigap policies are designed specifically to fill gaps in Original Medicare, not to function as standalone coverage. Attempting to purchase Medigap without both parts active will result in immediate denial of your application.
Navigating State-Specific Availability Rules
While Medigap policies are available in most states, specific regulations and plan options vary by location. Some states have additional consumer protections or different enrollment rules that affect how and when you can purchase coverage. Private insurance companies must be licensed to sell Medigap in your state, meaning certain national insurers might not operate in your area. Checking your state’s insurance department website reveals which companies offer Medigap policies where you live and any state-specific protections that apply to your coverage.
The Step-by-Step Process of How Medicare Supplement Works
Understanding the mechanics of how Medicare supplement works reveals why beneficiaries call these policies their financial safety net. When you receive medical care with Medigap coverage, a precise sequence of payments occurs that minimizes your out-of-pocket responsibility.
The Automatic Payment Coordination System
When you visit a doctor or hospital that accepts Medicare, you present both your red, white, and blue Medicare card and your Medigap insurance card. The provider bills Medicare first for the services rendered. Medicare processes the claim and pays its portion according to Part A or Part B coverage rules. Then, automatically and without any action required on your part, your Medigap policy pays its share directly to the provider. You only pay any remaining amounts specified by your particular Medigap plan—often nothing at all for covered services.
Standardized Plan Types With Identical Core Benefits
Medigap policies come in ten standardized plan types labeled A through N, each offering a specific combination of benefits. Crucially, Plan G from one insurer offers identical core coverage as Plan G from another company—the only differences lie in pricing and customer service. This standardization makes comparison shopping possible since you’re evaluating identical benefits across different insurers. Some plans cover all three gap categories (copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles), while others cover only specific costs, allowing you to match coverage to your healthcare needs.
Timing Your Medigap Enrollment for Best Results

Knowing when to secure coverage significantly impacts how Medicare supplement works for your financial protection and what you’ll pay long-term.
Your Six-Month Guaranteed Access Window
The Medigap Open Enrollment Period begins the moment you’re both 65 or older AND enrolled in Medicare Part B, lasting exactly six months. During this period, insurers cannot deny you coverage or charge higher premiums based on health conditions. This guaranteed issue right represents your best opportunity to obtain comprehensive Medigap coverage at standard rates. Waiting beyond this window means insurers can use medical underwriting to determine eligibility and pricing, potentially excluding pre-existing conditions or charging significantly higher premiums.
Critical Timing Considerations for Maximum Savings
Premiums for Medigap policies often increase substantially the longer you wait to enroll. Those who purchase Plan G at age 65 typically pay $150-$200 monthly, while waiting until age 70 could increase that premium by 30-50% due to attained-age rating practices. Understanding how Medicare supplement works includes recognizing that delaying enrollment not only risks higher costs but could leave you vulnerable to medical bills during the waiting period. Most financial advisors recommend securing Medigap coverage during your initial enrollment window to lock in the lowest possible rates.
Comparing Medigap Options Without Confusion
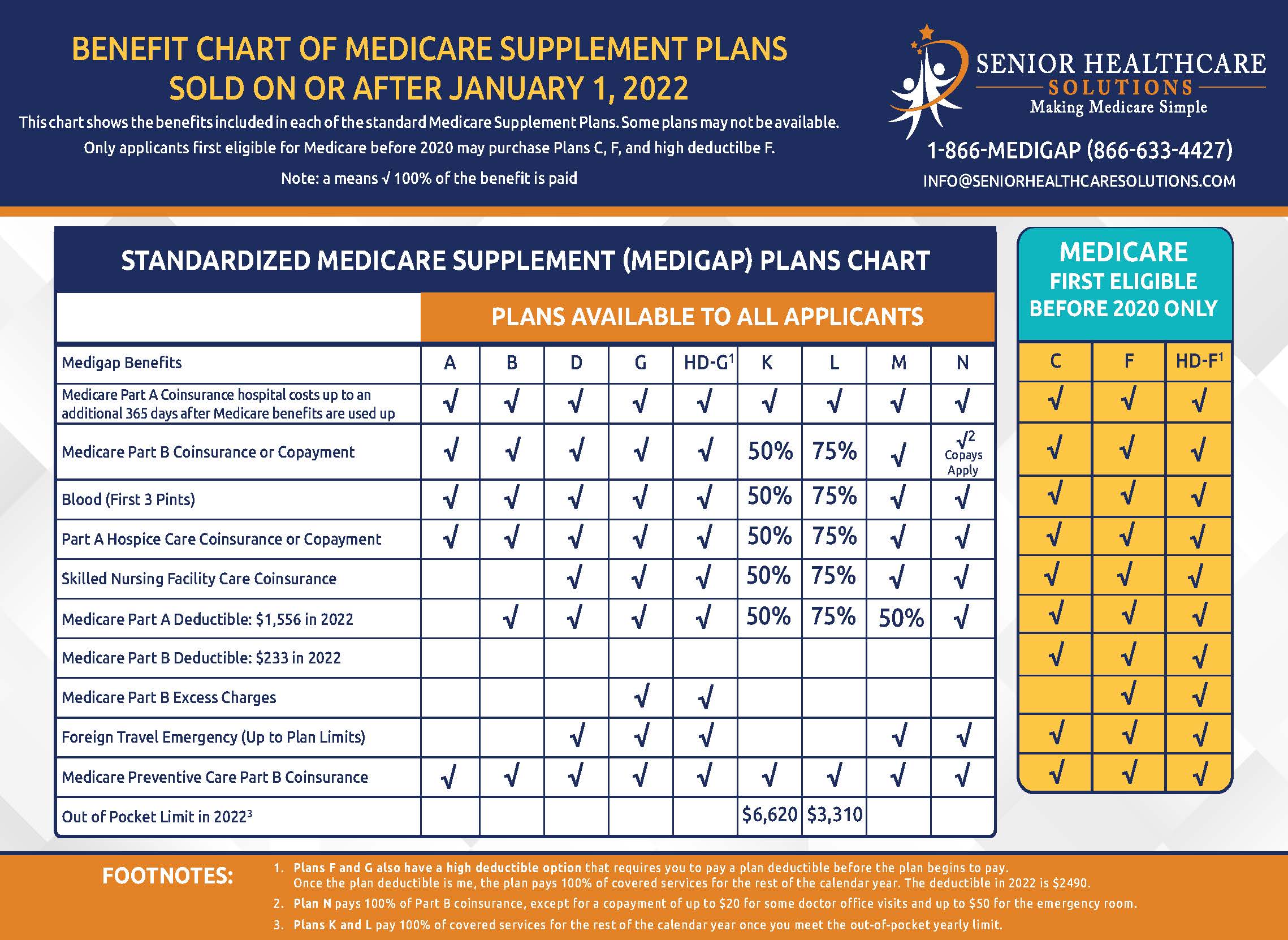
Selecting the right Medigap policy requires evaluating both coverage needs and long-term cost implications.
Premium vs. Out-of-Pocket Cost Tradeoffs
Plans with more comprehensive coverage (like Plan G or Plan F) carry higher monthly premiums but minimize your out-of-pocket costs when receiving care. Conversely, lower-premium plans (like Plan N) require you to pay small copayments for certain services but work well if you rarely need medical attention. Calculate your total expected healthcare spending by adding your estimated annual out-of-pocket costs under Original Medicare to potential Medigap premiums—this reveals which plan offers true savings based on your health situation.
Three Essential Comparison Factors Beyond Premiums
When evaluating how Medicare supplement works across different insurers, consider these often-overlooked factors:
– Pricing method: Community-rated (same price for all ages) vs. attained-age (increases as you age)
– Claims processing speed: Some insurers pay provider claims within days while others take weeks
– Customer service reputation: Check independent reviews for responsiveness during billing issues
Taking Action to Secure Your Medigap Coverage
Now that you understand how Medicare supplement works, implementing this knowledge protects your financial security.
Immediate Next Steps for Eligible Beneficiaries
If you’re within your six-month Open Enrollment Period, gather quotes from at least three insurers offering the same Medigap plan type in your area. Use the Medicare Plan Finder tool at Medicare.gov to compare standardized benefits, then contact insurers directly for personalized premium quotes. Review each proposal’s pricing methodology to understand how costs might change over time—this prevents unpleasant surprises years later when premiums suddenly increase.
Maintaining Coverage Without Unnecessary Costs
Once enrolled, review your Medigap policy annually during Medicare’s Open Enrollment Period (October 15-December 7) to ensure it still matches your needs. While switching Medigap plans typically requires medical underwriting after your initial enrollment period, certain circumstances like moving to a new state or losing other coverage may trigger guaranteed issue rights that allow plan changes without health questions. Regular policy reviews ensure you’re not overpaying for coverage you no longer need while maintaining essential financial protection.
Understanding how Medicare supplement works transforms healthcare from a source of financial anxiety into a predictable expense you can confidently plan for. By bridging Original Medicare’s coverage gaps, Medigap policies provide the peace of mind that comes with knowing your retirement savings won’t vanish due to unexpected medical bills. Whether you’re newly eligible for Medicare or have carried coverage for years, regularly reviewing how Medicare supplement works ensures you maintain optimal protection against healthcare costs that could otherwise derail your financial security.