Millions of people unknowingly suffer from magnesium deficiency due to modern diets dominated by processed foods, depleted agricultural soils, and chronic stress that depletes this critical mineral. Despite being involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions throughout your body, magnesium often gets overlooked in daily nutrition conversations. When your magnesium levels fall below optimal ranges, you might experience muscle cramps, restless sleep, and persistent fatigue—symptoms many mistakenly attribute to aging or stress alone.
Understanding the science-backed magnesium dietary supplement benefits can transform your health journey. This essential mineral supports everything from your heartbeat rhythm to muscle recovery after exercise, from blood sugar regulation to stress resilience. The National Institutes of Health estimates that nearly half of all Americans don’t meet their daily magnesium requirements through diet alone. For those experiencing symptoms of deficiency or seeking to optimize their health, magnesium supplementation offers a research-supported solution with minimal risk when used appropriately.
How Magnesium Powers Over 300 Biochemical Reactions

Magnesium acts as a cofactor for enzymes driving essential physiological processes you depend on daily. This mineral enables protein synthesis for muscle repair, regulates nerve impulses that control every movement you make, and maintains healthy blood glucose levels that prevent energy crashes. Without sufficient magnesium, your cellular energy production falters since the mineral plays a central role in creating ATP—the energy currency powering every cell in your body.
The mineral’s regulatory function extends to controlling calcium and potassium movement across cell membranes, a process critical for maintaining proper heart rhythm, muscle contraction, and nerve signaling. Approximately 60% of your body’s magnesium resides in your bones, supporting skeletal strength while the remainder distributes throughout soft tissues and bodily fluids. Modern lifestyles accelerate magnesium depletion through chronic stress that increases urinary excretion, medications like proton pump inhibitors that reduce absorption, and agricultural practices that have stripped soils of this vital nutrient.
Prevent Heart Palpitations and Support Cardiovascular Health
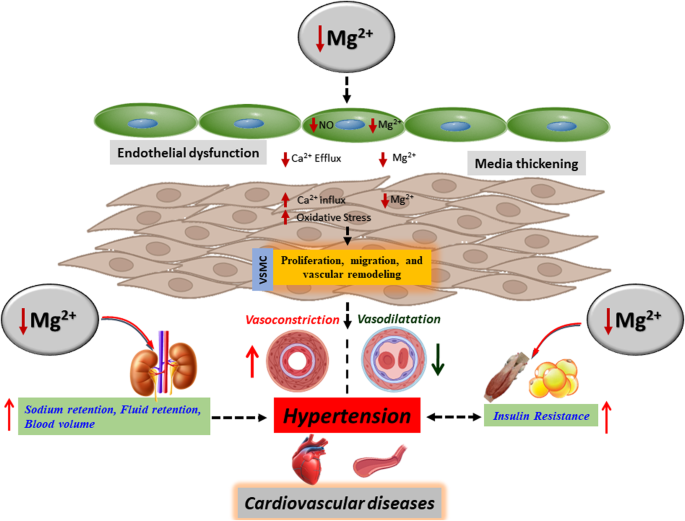
Magnesium dietary supplement benefits for heart health operate through multiple protective mechanisms that many people overlook. The mineral stabilizes electrical activity in cardiac tissue, preventing dangerous arrhythmias that could lead to stroke or cardiac events. Research consistently shows that individuals maintaining optimal magnesium levels demonstrate significantly lower risks of developing cardiovascular disease compared to those with deficiency.
This essential mineral promotes healthy blood pressure by encouraging blood vessel relaxation—a process called vasodilation that allows blood to flow with less resistance. Magnesium functions as a natural calcium channel blocker, preventing excessive calcium buildup in arterial walls that causes stiffness and elevated readings. Clinical studies reveal that supplementing with magnesium reduces both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, particularly in those with existing hypertension.
Beyond blood pressure management, magnesium supports healthy cholesterol metabolism and reduces systemic inflammation that damages blood vessel linings. For those with metabolic syndrome or multiple cardiovascular risk factors, magnesium supplementation represents an accessible, evidence-based strategy that works synergistically with other heart-healthy interventions.
Stop Muscle Cramps and Accelerate Post-Workout Recovery
Athletes and active individuals experience dramatic improvements in performance and recovery through strategic magnesium supplementation. The mineral regulates the delicate balance between muscle contraction and relaxation by controlling calcium uptake into muscle cells—when magnesium levels drop, excessive calcium causes prolonged contraction leading to painful cramps and spasms. By ensuring proper calcium handling, magnesium helps prevent those sudden calf cramps that wake you at night or hamstring pulls during exercise.
Intense physical activity significantly increases magnesium demand while simultaneously depleting stores through sweat. Without adequate replacement, you face decreased athletic performance, prolonged muscle soreness, and higher injury risk. Supplementing with magnesium before and after workouts supports your body’s adaptation to training stress while minimizing exercise-induced oxidative damage that delays recovery.
The muscle-relaxing properties of magnesium extend beyond athletic performance to everyday comfort. Those suffering from chronic tension headaches, stiff necks, or lower back pain often find substantial relief through consistent magnesium intake, as the mineral promotes relaxation of both smooth and skeletal muscles throughout your body.
Fix Sleep Problems and Reduce Stress Naturally
Magnesium powers your body’s transition from daytime alertness to nighttime restoration by activating the parasympathetic nervous system responsible for “rest and digest” functions. This essential mineral regulates melatonin production—the hormone guiding your sleep-wake cycles—while simultaneously reducing cortisol levels that keep you wired when you should be winding down. Clinical trials demonstrate that magnesium supplementation helps people fall asleep faster, stay asleep longer, and experience deeper, more restorative sleep cycles.
The calming effects of magnesium extend to daytime stress management through its regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. When this stress response system becomes overactive, you experience anxiety, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Magnesium supplementation helps modulate HPA axis activity, reducing hyperarousal while promoting emotional balance. Many users report feeling noticeably calmer within days of starting magnesium, with improvements in both sleep quality and daytime resilience to stressors.
Why Your Blood Sugar Regulation Depends on Magnesium
Magnesium plays a dual role in maintaining healthy blood glucose levels by influencing both insulin secretion and sensitivity. The mineral stimulates pancreatic beta cells to release appropriate amounts of insulin while simultaneously enhancing cellular response to this critical hormone. Without sufficient magnesium, your body struggles to process carbohydrates efficiently, leading to blood sugar spikes and crashes that contribute to insulin resistance over time.
Research consistently shows that higher magnesium intake correlates with significantly lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. For those already managing blood sugar concerns, magnesium supplementation improves glycemic control and reduces medication requirements. The mineral also supports healthy weight management by influencing appetite regulation hormones and metabolic rate—making it particularly valuable for those with metabolic syndrome or prediabetes.
Choose the Right Magnesium Form for Your Specific Needs
Not all magnesium supplements deliver equal benefits—selecting the appropriate form based on your health goals dramatically impacts results. Magnesium glycinate binds the mineral to glycine, an amino acid that enhances relaxation and sleep quality while causing minimal digestive disturbance. This highly bioavailable form works best for stress reduction, sleep support, and general supplementation.
Magnesium citrate offers good absorption at lower cost while providing mild laxative effects that benefit occasional constipation. Though well-absorbed, citrate may cause loose stools in sensitive individuals, making it suitable for general magnesium repletion without specific sleep goals. Magnesium oxide contains high elemental magnesium concentration but suffers from poor bioavailability, remaining primarily in the digestive tract to draw water osmotically—ideal for constipation relief but less effective for systemic repletion.
Optimize Your Magnesium Dosage and Timing Strategy
The recommended daily allowance for magnesium ranges from 310-420 milligrams depending on age and sex, though therapeutic applications often require higher doses under professional guidance. Rather than taking a single large dose, split your intake throughout the day—morning, midday, and evening—to maximize absorption and minimize digestive effects.
Those using magnesium primarily for sleep benefit from taking their largest dose 30-60 minutes before bedtime, while athletes may time doses around workouts to support muscle function and recovery. Taking magnesium with food enhances tolerance, particularly for forms like citrate that can stimulate digestive activity. Start with moderate doses and gradually increase while monitoring your body’s response to identify your optimal amount.
Recognize Hidden Magnesium Deficiency Symptoms
Magnesium deficiency often goes undiagnosed because standard blood tests measure only the 1% of magnesium circulating in blood—not your total body stores. Early deficiency manifests as muscle twitches, cramps, and spasms—particularly in eyelids, face, or calves—alongside fatigue, weakness, and loss of appetite. These subtle symptoms frequently get misattributed to other causes, delaying recognition of underlying depletion.
Advanced deficiency can cause abnormal heart rhythms, coronary spasms, seizures, and personality changes. Chronic low magnesium status has been linked to osteoporosis, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and migraines. If you experience persistent muscle cramps, restless sleep, or unexplained fatigue—especially if you take medications like proton pump inhibitors or diuretics—you may benefit from magnesium supplementation.
Maximize Supplement Effectiveness with These Proven Strategies
Enhance magnesium absorption by combining it with vitamin D3, as these nutrients work synergistically—vitamin D boosts intestinal magnesium uptake while magnesium enables vitamin D activation. Take these supplements together with a small amount of dietary fat for optimal absorption. Avoid consuming magnesium simultaneously with high-calcium foods or supplements, as these minerals compete for absorption pathways; separate intake by two or more hours.
Select supplements verified by third-party testing organizations like USP, NSF International, or ConsumerLab to ensure accurate ingredient labeling and absence of contaminants. Products manufactured in FDA-registered facilities following current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) offer higher quality assurance than those from unregulated operations.
Final Note: Consistent magnesium supplementation delivers wide-ranging benefits for cardiovascular function, muscle performance, sleep quality, and metabolic health when matched to your specific needs. Choosing the appropriate form—glycinate for relaxation, citrate for general support, or malate for energy—combined with strategic timing and dosing, creates a powerful foundation for optimal health. By addressing this common nutritional gap, you empower your body’s 300+ enzymatic processes to function at their best, supporting vitality and resilience that extends far beyond individual symptoms to enhance your overall quality of life.




