Waking up stiff and sore after an intense workout? Your body might be missing a critical recovery window during sleep. When you drift off for the night, your body enters an extended fasting state that can trigger muscle breakdown for up to 8 hours. By strategically taking protein supplement before bed, you flood your system with slow-digesting amino acids that combat this catabolic process and fuel muscle repair throughout the night. Research shows nighttime protein consumption boosts muscle protein synthesis rates by up to 22% compared to going to bed without protein, making it a game-changer for athletes and fitness enthusiasts seeking maximum results.
The market has responded with specialized formulas that combine protein with sleep-enhancing nutrients—going beyond basic protein powders to address both physical recovery and rest quality. Unlike post-workout whey protein designed for rapid absorption, bedtime formulas prioritize sustained amino acid delivery and relaxation compounds. Whether you’re a competitive athlete optimizing performance or someone struggling with morning stiffness, understanding how protein supplement before bed works can transform your recovery strategy and overall well-being.
Why Your Muscles Need Protein During Sleep
The Overnight Muscle Breakdown Problem
During waking hours, you typically consume meals every few hours, keeping amino acids flowing to your muscles. This changes dramatically when you sleep—the 8+ hours between dinner and breakfast creates an extended fast where your body shifts toward catabolic processes. Without external protein sources, your system starts breaking down muscle tissue to access amino acids for energy and metabolic functions. This overnight muscle protein breakdown can undermine your training efforts, especially if you’ve been pushing hard in the gym.
Consuming protein supplement before bed directly counteracts this catabolic state by providing exogenous amino acids specifically for muscle repair during sleep. Studies confirm that nighttime protein intake increases muscle protein synthesis rates during sleep compared to going to bed without protein. The key is choosing a protein type that releases amino acids gradually rather than all at once, sustaining this benefit throughout your entire sleep cycle.
Extending Your Anabolic Window Through the Night
The traditional “anabolic window” concept focused narrowly on the immediate post-workout period, but modern research reveals muscle sensitivity to protein extends far beyond this timeframe. Your body remains in an anabolic, receptive state for many hours after exercise—including throughout the night during sleep. By providing protein supplement before bed, you effectively extend this anabolic period to cover your entire sleep duration.
This strategy proves especially valuable if you train in the evening and have several hours between your last meal and bedtime. Instead of going to bed in a fasted state that promotes muscle breakdown, you proactively support recovery while you sleep. The cumulative effect of consistent nighttime protein supplementation delivers significant improvements in muscle mass, strength, and recovery capacity over weeks of training.
Casein Protein: The Overnight Recovery Powerhouse
How Casein’s Slow Digestion Works Overnight
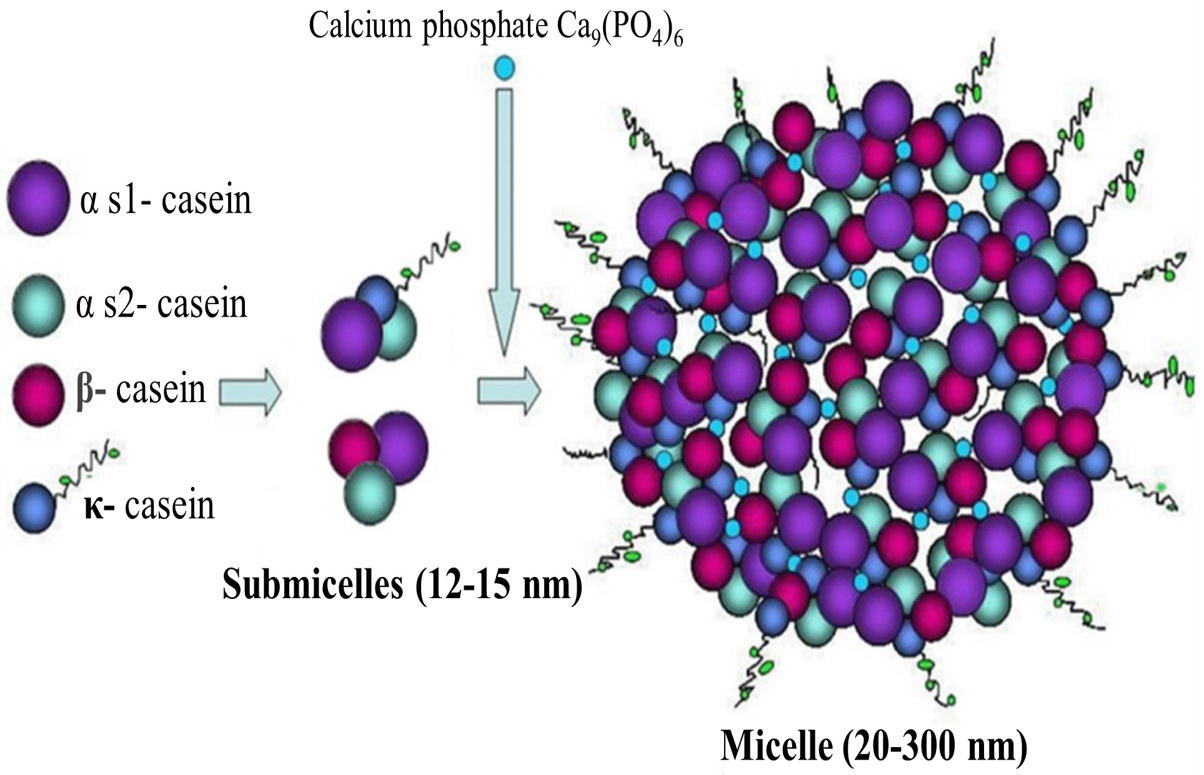
Casein protein, making up approximately 80% of milk protein, possesses unique properties perfect for nighttime use. Unlike whey protein absorbed within 1-2 hours, casein forms a gel-like substance in your stomach that releases amino acids gradually over 4-6 hours. This slow-release mechanism ensures a steady trickle of amino acids throughout the night when you’d otherwise experience prolonged nutrient deprivation.
The science behind casein’s effectiveness: In your stomach’s acidic environment, casein coagulates or clumps, delaying gastric emptying. This means the protein stays in your digestive system longer, steadily releasing amino acids into your bloodstream. The result? A stable blood amino acid profile that continues supporting muscle protein synthesis even during deep sleep stages when metabolism slows.
Casein vs. Whey: Which Works Better Before Bed?

While whey protein shines as a post-workout supplement due to rapid absorption and high leucine content, it often falls short for nighttime use. Whey creates a rapid spike in blood amino acids followed by an equally rapid decline—leaving muscle tissue without adequate support during later sleep hours. Casein’s slow-digesting nature solves this problem directly.
Many effective nighttime formulas use an 80/20 casein-to-whey ratio to maximize benefits:
– Casein component provides sustained amino acid release throughout the night
– Whey component delivers an initial rapid amino acid spike for immediate muscle protein synthesis
– Combined effect creates comprehensive overnight muscle support
This strategic blend leverages the best of both proteins—whey’s quick action to kickstart recovery and casein’s slow release to maintain it through morning.
How Bedtime Protein Improves Sleep Quality
The Muscle Recovery-Sleep Connection
The primary benefit of protein supplement before bed extends beyond muscle growth—it enhances overall recovery quality. When you strength train, you create microscopic damage to muscle fibers. It’s during rest periods, particularly sleep, that your body repairs this damage and emerges stronger. Providing adequate protein support during this critical period accelerates repair and improves recovery quality.
Studies tracking pre-sleep protein consumption show participants taking 30-40 grams of casein before bed experienced significantly higher overnight muscle protein synthesis rates compared to placebo groups. Over time, this translates to better muscle mass gains, increased strength, and reduced soreness. Regular users often report waking up feeling more recovered and ready for their next training session.
Sleep-Supporting Ingredients That Make the Difference
Many specialized nighttime protein formulas include compounds specifically designed to enhance sleep quality alongside protein. These formulations combine protein with ingredients like:
– GABA to promote relaxation by inhibiting overactive nerve signals
– L-Theanine for calm without sedation (found naturally in tea)
– Magnesium glycinate supporting muscle relaxation and nervous system calm
– Tryptophan or 5-HTP as precursors to serotonin and melatonin
Unlike melatonin supplements that can cause morning grogginess, these protein-focused sleep aids work with your body’s natural processes. Users frequently report falling asleep faster, staying asleep throughout the night, and waking up feeling genuinely refreshed—without the “hangover” effect of traditional sleep aids.
Choosing the Right Nighttime Protein Formula

Evaluating Protein Ratios and Sources
When selecting a protein supplement before bed, the protein type and ratio significantly impact effectiveness. Milk protein isolate—combining casein and whey in natural proportions—serves as the foundation of many effective nighttime formulas. This provides both slow-digesting casein benefits and whey’s rapid absorption and high leucine content.
Look for products that clearly specify their protein ratios:
– Pure casein formulas maximize slow-digestion benefits but may lack rapid amino acid spikes
– 80/20 casein-to-whey blends offer a popular middle ground with immediate and sustained delivery
– Plant-based alternatives (like pea protein) exist but typically lack casein’s slow-digesting properties
Understanding these differences helps you select a product aligned with your specific recovery goals and preferences.
Quality Certifications That Matter
Due to the supplement industry’s relatively light regulation, third-party testing and certifications are crucial. Prioritize products:
– Manufactured in cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practice) certified facilities
– Verified through NSF certification for purity and accurate labeling
– Produced in countries with stringent regulatory frameworks (like the United States)
These certifications don’t guarantee effectiveness but indicate the manufacturer invests in quality systems and submits to external scrutiny—particularly important for products containing multiple bioactive ingredients.
Optimal Timing and Dosage Strategies
When to Take Your Bedtime Protein
Consume your protein supplement 30-60 minutes before bedtime to allow digestion to begin while letting relaxation effects take hold. This timing ensures digestion is underway by sleep time, reducing discomfort risk that could interfere with sleep quality.
Individual variation affects optimal timing—some prefer taking protein earlier as part of their wind-down routine, while others consume it immediately before bed. Experiment to find what works best for your body, but prioritize consistency. Making pre-sleep protein consumption a nightly habit creates automaticity, ensuring you never miss this critical recovery window.
Finding Your Perfect Dosage
Research suggests 20-40 grams of protein per meal optimally stimulates muscle protein synthesis. Most bedtime protein formulas provide approximately 20 grams per serving, fitting within this effective range for overnight support. This dose delivers sufficient amino acids without excessive calories that might interfere with weight management goals.
Higher protein doses may benefit those in intense training phases, calorie restriction, or maximizing muscle gain. However, remember that total daily protein intake matters more than any single dose—ensure your bedtime protein complements rather than replaces other protein sources throughout your day.
Avoiding Common Nighttime Protein Mistakes
Don’t Ignore Digestive Sensitivity
Casein’s slow-digesting properties that make it effective for overnight support can cause discomfort if consumed too close to bedtime or in large quantities. If you experience heaviness or fullness:
– Try taking your protein earlier in the evening
– Gradually increase serving size rather than starting with maximum dose
– Consider simpler ingredient formulas if sensitive to artificial additives
Pro tip: Blend your protein with warm liquid for faster initial digestion or cold liquid for more gradual processing—experiment to find what works best for your digestive system.
Combine With Overall Nutrition Strategy
Bedtime protein works best as part of comprehensive nutrition—not a standalone solution. Ensure you’re consuming adequate protein throughout the day, distributed across multiple meals. The protein you take before bed should complement rather than replace your other protein feedings.
Track both subjective measures (sleep quality, morning energy, workout recovery) and objective metrics (workout performance, body composition changes) to determine if nighttime protein supplementation delivers value for your specific goals. Remember that many factors influence these outcomes, so patience is key—give your body time to adapt and respond before evaluating effectiveness.